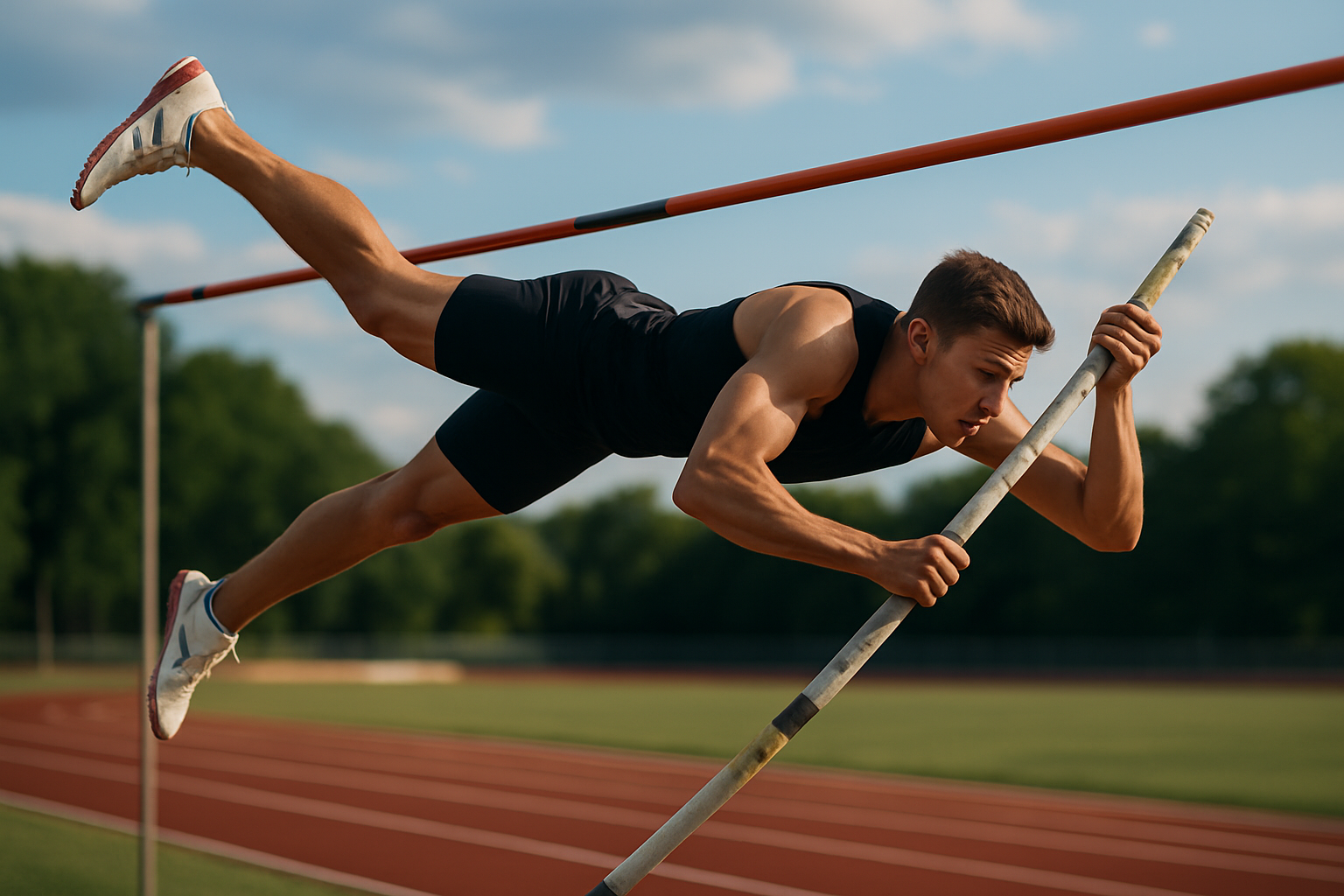
Competitive Pole Vaulting: Soaring to New Heights
The thunderous applause of the crowd fades into the background as the pole vaulter takes a deep breath, eyes fixed on the distant bar. With a burst of speed, they charge down the runway, plant the pole, and launch themselves skyward in a breathtaking display of strength, technique, and courage. This is the world of competitive pole vaulting, where athletes defy gravity and push the limits of human potential.

The Origins of Pole Vaulting
Pole vaulting’s roots can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where it served a practical purpose rather than a competitive one. In marshy regions of the Netherlands and Great Britain, locals used long poles to vault over canals and wetlands. Similarly, ancient Greeks and Cretans employed poles to scale walls during warfare.
The transition from utility to sport began in the 18th and 19th centuries. German gymnasts incorporated pole vaulting into their routines, while in Great Britain, it became a part of military training. The first recorded competitive pole vault event took place in 1850 at the Ulverston Football and Cricket Club in England.
The sport gained significant traction in the United States during the late 19th century, with colleges and athletic clubs organizing competitions. In 1896, pole vaulting made its Olympic debut at the first modern Games in Athens, Greece, solidifying its place in the world of track and field.
The Physics Behind the Vault
At its core, pole vaulting is a masterful application of physics principles. The sport involves converting horizontal kinetic energy into vertical potential energy, allowing athletes to propel themselves over a bar set at dizzying heights.
The vault begins with the approach run, where the athlete builds up speed and kinetic energy. As they plant the pole into the box, the flexible pole bends, storing elastic potential energy. The vaulter’s body position and timing are crucial at this point, as they must effectively transfer their momentum into the bending pole.
As the pole straightens, it releases its stored energy, launching the vaulter upward. The athlete then performs a series of complex movements, rotating their body to clear the bar. This phase requires immense core strength, spatial awareness, and precise timing.
Understanding these physical principles is essential for pole vaulters and their coaches, as it informs technique refinement and equipment selection. The interplay between the athlete’s speed, strength, and the pole’s characteristics determines the ultimate height achieved.
The Evolution of Pole Technology
The evolution of pole technology has played a significant role in the advancement of pole vaulting performances. Early vaulters used rigid poles made of wood, bamboo, or metal, which limited the heights that could be achieved.
A revolutionary change occurred in the early 1950s with the introduction of flexible fiberglass poles. These poles allowed vaulters to generate much greater bend, storing and releasing more energy during the vault. This innovation led to a dramatic increase in vault heights and fundamentally changed the technique of the sport.
Today’s poles are typically made from carbon fiber or a combination of carbon fiber and fiberglass. These materials offer an optimal balance of strength, flexibility, and weight. Modern poles are carefully engineered to match the vaulter’s weight, speed, and technique, allowing for maximum energy transfer and height potential.
The selection of the right pole is a critical aspect of a vaulter’s preparation. Factors such as the pole’s length, stiffness, and weight rating must be precisely matched to the athlete’s characteristics and skill level. Elite vaulters often travel with multiple poles to adapt to different competition conditions.
Techniques and Training Methods
Successful pole vaulting requires a unique combination of speed, strength, flexibility, and technical skill. Athletes must develop proficiency in several key areas to excel in this demanding sport.
The approach run is the foundation of a good vault. Vaulters typically use a run of 40-45 meters, gradually building speed while maintaining control. The final steps are crucial, as they set up the plant of the pole. Athletes spend countless hours perfecting their run-up, ensuring consistency in their stride pattern and speed.
The plant and take-off phase require precise timing and body positioning. Vaulters must seamlessly transition from horizontal motion to vertical ascent, driving their body upward as the pole bends. This phase demands explosive leg strength and core stability.
As the pole straightens, vaulters perform a complex series of movements known as the “swing-up” and “inversion.” These actions involve pulling the body upward, rotating to a vertical position, and pushing off the pole to clear the bar. Gymnastic ability and upper body strength are essential for executing these techniques effectively.
Training for pole vault is multifaceted, incorporating elements of sprint training, gymnastics, and weightlifting. Vaulters spend time in the weight room building overall strength and power. Plyometric exercises help develop explosive leg strength for the take-off. Gymnastic training, including work on rings and high bars, improves body awareness and control in the air.
Technical drills form a significant part of training, with athletes practicing each phase of the vault in isolation before combining them. Video analysis is commonly used to fine-tune technique and identify areas for improvement.
The Mental Game of Pole Vaulting
While the physical aspects of pole vaulting are undoubtedly demanding, the mental challenges of the sport are equally formidable. Vaulters must contend with fear, pressure, and the need for intense focus and concentration.
The inherent risk involved in launching oneself several meters into the air requires a significant degree of courage. Vaulters must trust their training, equipment, and technique as they attempt to clear ever-increasing heights. Overcoming the fear of falling or injury is a constant psychological battle for many athletes.
Competitive pressure adds another layer of mental challenge. In major competitions, vaulters often have only three attempts at each height. The ability to perform under pressure, managing nerves and maintaining focus, can make the difference between success and failure.
Visualization techniques are commonly employed by pole vaulters to prepare mentally for competition. Athletes spend time imagining successful vaults, rehearsing each phase of the jump in their mind. This mental practice can help build confidence and improve performance consistency.
Goal-setting is another crucial aspect of the mental game. Vaulters work with coaches to set realistic yet challenging targets for improvement. These goals provide motivation during training and a sense of accomplishment as they are achieved.
The Global Stage: Pole Vaulting in International Competition
Pole vaulting has been a staple of international track and field competitions since its inclusion in the 1896 Olympics. The sport features prominently in the Olympic Games, World Championships, and Diamond League circuit, attracting top athletes from around the globe.
In recent years, the level of competition in both men’s and women’s pole vaulting has reached new heights. The current men’s world record stands at an astonishing 6.21 meters, set by Sweden’s Armand Duplantis in 2022. On the women’s side, Russia’s Yelena Isinbayeva holds the world record at 5.06 meters, a mark set in 2009.
The introduction of women’s pole vault to the Olympic program in 2000 marked a significant milestone for the sport. Since then, female vaulters have made remarkable progress, with performances approaching those of their male counterparts.
International competitions showcase not only individual talent but also the global nature of the sport. Countries such as the United States, Russia, France, and Germany have traditionally been strong in pole vaulting, but recent years have seen emerging powers like Sweden and Brazil producing world-class vaulters.
The Impact of Technology and Innovation
As with many sports, technology has had a profound impact on pole vaulting. Beyond the evolution of pole materials, advancements in other areas have contributed to improved performances and safety.
Landing areas have seen significant improvements over the years. Modern landing pits use high-density foam and air-filled chambers to provide a soft, safe landing for vaulters. These improvements have allowed athletes to attempt higher vaults with reduced risk of injury.
Video analysis tools have become invaluable for both training and competition. High-speed cameras allow coaches and athletes to break down each phase of the vault in minute detail, identifying areas for technical improvement. During competitions, video review systems are used to assist judges in making accurate decisions on bar clearances.
Wearable technology is increasingly being incorporated into training regimens. Sensors can provide data on an athlete’s run-up speed, take-off angle, and body position during the vault. This information helps coaches and athletes optimize technique and track progress over time.
3D motion capture technology is also being explored as a tool for biomechanical analysis. By creating detailed digital models of vaulters in action, researchers can gain new insights into the mechanics of successful vaults, potentially informing future training methods and technique development.
The Future of Pole Vaulting
As pole vaulting continues to evolve, several trends and developments are shaping the future of the sport.
Height progression remains a central focus. With the men’s world record now exceeding 6 meters, speculation abounds about the ultimate limits of human performance in the event. Some experts believe that a 7-meter vault may be possible with further advancements in technique and technology.
The globalization of the sport is likely to continue, with more countries investing in pole vaulting programs. This increased participation could lead to greater competition and potentially new techniques or training methods emerging from different parts of the world.
Environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in pole vaulting. Indoor competitions, which offer controlled conditions, are growing in popularity. Outdoor events are exploring ways to mitigate the effects of wind and weather on performances, potentially through the use of wind screens or other innovations.
Youth development is another area of focus for the sport’s governing bodies. Initiatives to introduce pole vaulting to younger athletes in a safe and accessible manner could help broaden the talent pool and secure the sport’s future.
The Community and Culture of Pole Vaulting
Beyond the competitive aspect, pole vaulting has fostered a unique and close-knit community. The shared experiences of facing fears, overcoming challenges, and pushing physical limits create strong bonds among vaulters.
Pole vault camps and clinics have become popular, bringing together athletes of all levels to learn from experienced coaches and elite vaulters. These events not only provide technical instruction but also serve as networking opportunities and a chance to share the passion for the sport.
Social media has played a role in connecting the global pole vaulting community. Platforms like Instagram and YouTube allow vaulters to share training tips, celebrate achievements, and support one another across geographical boundaries.
The sport has also inspired artistic expression, with pole vaulting featured in photography, sculpture, and even poetry. These creative works capture the grace, power, and drama inherent in the act of vaulting, helping to promote the sport to a wider audience.
Challenges and Controversies
Like any sport, pole vaulting faces its share of challenges and controversies. Safety concerns remain at the forefront, with ongoing discussions about equipment standards, landing area designs, and competition protocols to minimize the risk of injury.
The issue of gender equality in pole vaulting continues to be debated. While women’s pole vault has made great strides since its Olympic inclusion, disparities still exist in some areas, including prize money and media coverage at certain events.
Doping has affected pole vaulting, as it has many other sports. Several high-profile cases have led to increased scrutiny and testing. The sport’s governing bodies continue to work on maintaining the integrity of competitions and ensuring a level playing field for all athletes.
Environmental impact is an emerging concern, particularly regarding the disposal of broken or worn-out poles. The composite materials used in modern poles are not easily recyclable, leading to discussions about sustainable alternatives or improved recycling methods.
Conclusion: The Enduring Appeal of Pole Vaulting
Competitive pole vaulting stands as a testament to human ambition and the relentless pursuit of excellence. It is a sport that combines raw athleticism with technical precision, courage with calculated risk-taking. From its humble origins to its current status as a marquee event in track and field, pole vaulting continues to captivate athletes and spectators alike.
The unique challenges posed by pole vaulting—the constant battle against gravity, the split-second timing required for success, the mental fortitude needed to launch oneself skyward—ensure its enduring appeal. As records continue to fall and new generations of vaulters emerge, the sport remains a powerful symbol of human potential and the heights we can achieve, both literally and figuratively.
For those who have experienced the thrill of a successful vault, clearing the bar and floating momentarily above the world, the allure of pole vaulting is undeniable. It is a sport that pushes the boundaries of what is possible, inspiring us all to reach higher and dream bigger. As we look to the future, one thing is certain: the world of competitive pole vaulting will continue to soar to new and exciting heights.